United States: The research team recently had about 30 percent of the adult population in the world not having a period lasting from 7-8 hours for sleep and, as a result, suffer from different sleep experiences at night.
The disease that was not previously noticed but due to extensive reliance on alcohol in the US community, where not more than 25 percent of adults are the sufferers of it, is the cause of the “silent epidemic.”
More about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
The word “fatty” can be described as NAFLD, which is a disease with fat in the liver. There are two reasons for it - obesity, which is a factor of a disturbed metabolism including metabolic syndromes like diabetes 2, high blood pressure, raised triglyceride levels, and obstructive sleep apnea - that is found out by gastroenterologist Ibrahim Hanouneh of MNGI Digestive Health in Minnesota.
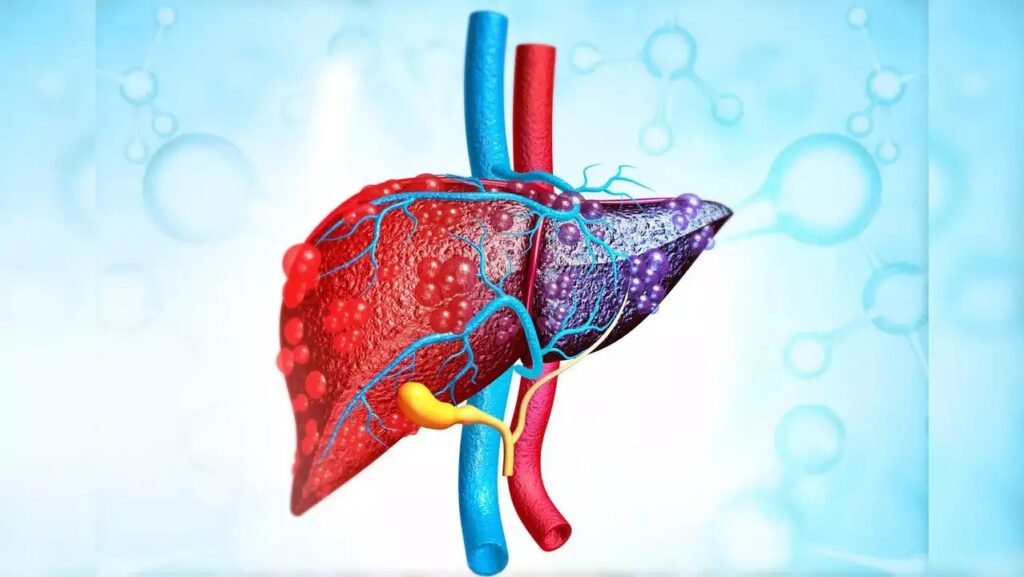
Hanouneh said,” foolish consumption of alcohol can also cause fatty liver, but if an individual has fatty liver, which is common in the setting metabolic syndrome and heavyweight in the absence of excessive alcohol use, it’s called NAFL,” as Fox News reported.
Furthermore, the condition can sometimes also be referred to as MASLD (metabolic dysfunction associated with steatotic liver disease), which showcases a link between fatty liver and metabolic syndrome.
Does NAFL have any symptoms?
Additionally, NAFL is termed a “silent epidemic” since no symptoms are associated with it.
Hanouneh added, “In some studies, fatty liver has affected 25% to 33% of the general population — almost one out of four individuals — but the vast majority of individuals have no symptoms at all, particularly in the early stages,” as Fox News reported.
However, few people might exhibit non-specific symptoms, such as fatigue, foggy memory, and abdominal pain.
Hanouneh added, “Generally speaking, the fatty liver disease does not cause major symptoms until it is too late, for example, when the patient has already developed cirrhosis or liver cancer.”
Moreover, possessing a fatty liver disease is linked to an increasing amount of risk related to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Hanouneh noted, “NAFLD has become the leading indication of liver transplantation and the leading cause of liver cancer in the Western world,” where such patients have a rising risk of cardiovascular-related illnesses, like heart attacks and strokes.